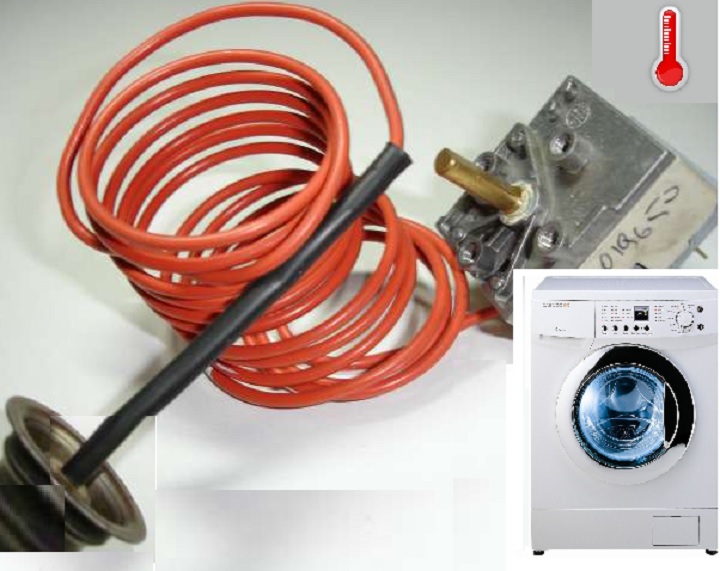
 The temperature sensor is a part inside the machine, which is responsible for the temperature of the water and the work of the heating element.
The temperature sensor is a part inside the machine, which is responsible for the temperature of the water and the work of the heating element.
In the event that overheating occurs or the water does not start heating at all, the thermostat will be to blame, which sends readings to the automatic control system to shut down the temperature heating in time.
Let's look at the problems associated with the thermostat sensor in this article.
Types of Thermostats
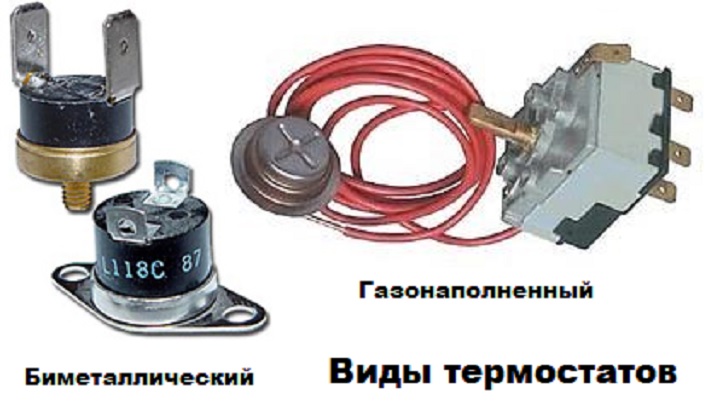 There are many models of washing machines and not all have the same sensor design.
There are many models of washing machines and not all have the same sensor design.
They are divided into electromechanical, which are divided into:
- bimetallic;
- gas-filled.
Electromechanical sensors.
Their work is that they open the electrical circuit when the set temperature is reached.
Gas-filled
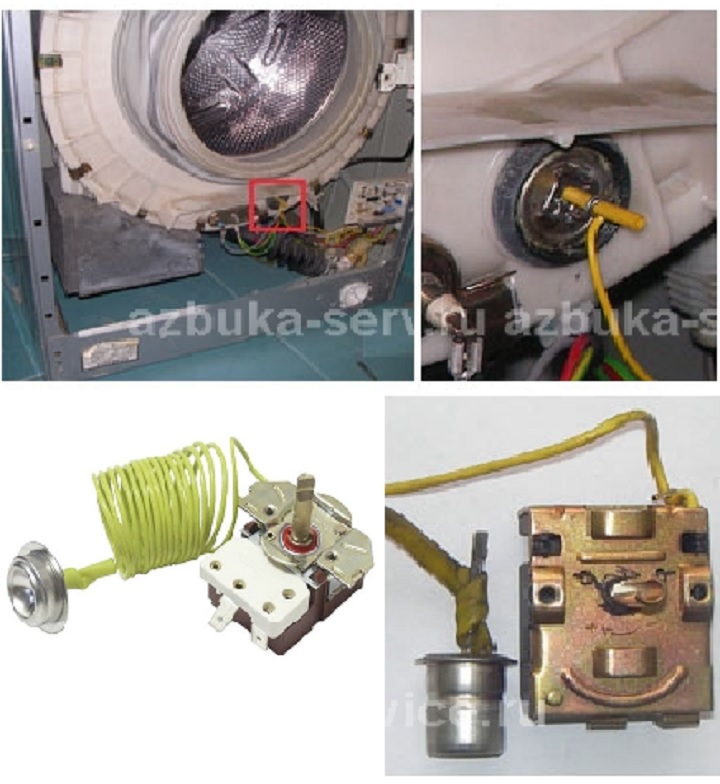 Such a sensor is divided into two halves. The first looks like a tablet of metal up to 30 mm in size and height of 30 mm.
Such a sensor is divided into two halves. The first looks like a tablet of metal up to 30 mm in size and height of 30 mm.
This part is located on the inside of the tank of the machine and is in direct contact with water.
The other part looks like a copper tube that connects to the temperature regulator that we see on the control panel.
This thermostat is filled with freon. As the water temperature changes, it expands or contracts and this causes the contacts of the heating element to close or open.
Bimetallic
Also looks like a tablet of the same size, about 30 mm, but the height is not more than 10 mm.
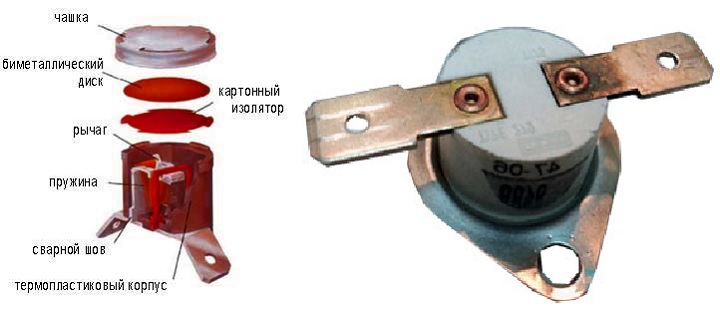 It received its name because of the bimetallic plate located inside.
It received its name because of the bimetallic plate located inside.
When the water heats up to the desired temperature, the plate of metal bends and it allows you to close contacts so that the heating stops.
Electronic sensor
We will be talking about a thermistor. Installed in almost all current models of washing machines and dishwashers.
This is a long (30 mm) cylinder of metal or a rod with a diameter of 10 mm.
It is located directly on the heating element. The thermistor reacts to changes in resistance when heating water to a temperature set by the regulator and, when the desired values are reached, gives the command to turn off the heating process.
How do I check the temperature sensor of my washing machine?
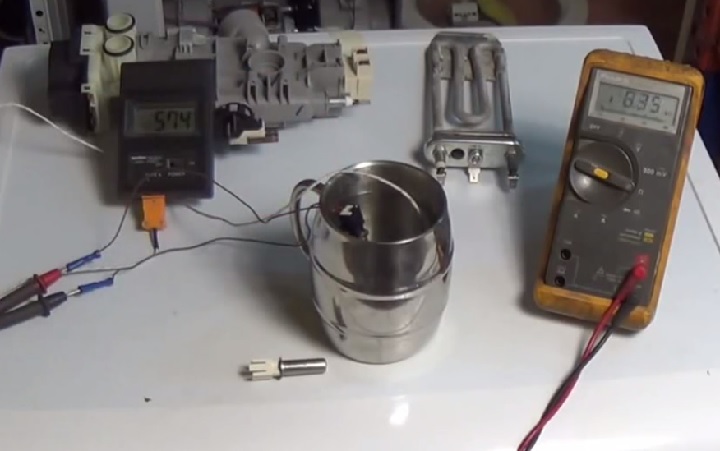 To make sure the part is malfunctioning, you'll have to take it out.
To make sure the part is malfunctioning, you'll have to take it out.
Often the electronic thermistor is located inside the heater, which is on the bottom of the washing machine.
Checking your washing machine's thermistor is not difficult. First you have to take it out, and to get it out you will have to:
- Remove the back cover;
- Unplug the wires from the sensor;
- Unscrew the screw that holds the heating element;
- take out the thermistor.
Multimeter readings
The multimeter should show a resistance of 6000 ohms if the temperature is 20 degrees.
Although multimeter readings are very relative. It is necessary to be guided by the model of the washing machine:
- У Zanussi, Electroulux Zanussi Electroulux at 30 degrees, the resistance is about 17 kohms.
- The temperature sensor of the washing machine Ardo will show 5.8 kOhm in normal mode.
- У Kandi has 27 kOhms under the same condition.
Now you need to put the thermistor in 50 degree water and check it. The resistance should drop to 1350 ohms (depending on the model).
To find out exactly what the reading should be, you need to look in the description of the machine or on the manufacturer's website.
Checking the gas sensor
The gas sensor is a little more difficult to get to.
You will have to remove the back cover and the front control panel. On the control panel, you have to unscrew the outer part of the sensor. On the back you should see the lead with wires.
 It is very important to avoid damaging the copper tube, so you have to get rid of the rubber insulation very carefully.
It is very important to avoid damaging the copper tube, so you have to get rid of the rubber insulation very carefully.
You can arm yourself with an awl to pick up the seal around the tube and remove it. To get the sensor out of the groove, you have to apply a little pressure, pull it out, and unhook the wires.
A common breakdown for such a sensor is a problem with the copper tubing from which the freon comes out and replacing the thermostat in the washing machine.
Checking the Bimetallic Sensor
The bimetallic sensor is in the same place as the gas sensor, and is taken out similarly.
It is checked with a multimeter and then heated in hot water, as with a thermistor. Basically, in such a sensor the cause of inoperability is in the plate, its wear or mechanical damage. When it malfunctions, it is replaced with a new one.
How to understand that the sensor is broken?
There are external signs that allow you to say with certainty that the problem is in the sensor. These include:
- The machine even on the low temperature mode heats water to boiling.
- The body of the machine heats up during operation, and you can see steam coming out of the hatch.





